Neurotransmitters and Brain Health: Achieving Balance with Essential Nutrients
What are Neurotransmitters in the Brain and What Roles do they play in Focus, Energy and Mood?
Neurotransmitters are chemical messengers that facilitate communication between nerve cells in the brain. Their balanced levels are crucial for optimal brain health and function. Imbalances in neurotransmitters can contribute to various neurological conditions and affect mood, cognition, and overall well-being. In this article, we will explore the role of different neurotransmitters in the brain and how specific nutrients, including vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, and B12, as well as iron, copper, vitamin D, vitamin C, SAM-E, and folate, support their conversion and balance. Understanding this intricate relationship can help us prioritize brain health and support neurotransmitter optimization.
Neurotransmitters and Their Functions:
1. Serotonin:
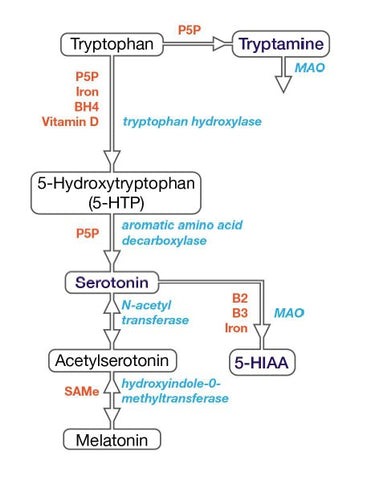
Serotonin, often referred to as the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, is pivotal for mood regulation, sleep, and appetite. It is synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan, a process facilitated by Vitamin B6. This nutrient is crucial in converting tryptophan into serotonin, ensuring the maintenance of healthy serotonin levels. Elevated serotonin levels are associated with improved mood and emotional well-being.It plays a crucial role in mood regulation, sleep, and appetite.
Conversion Nutrients:
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 is required to convert tryptophan (an amino acid) into serotonin. It helps support healthy serotonin levels.
2. Dopamine:
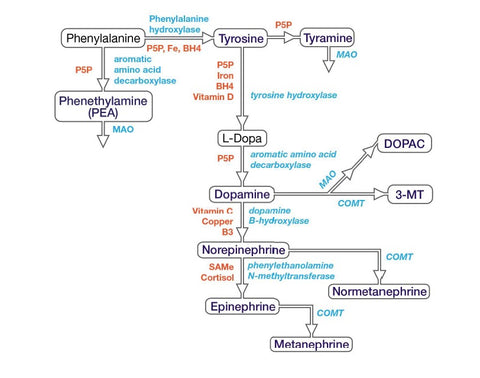
Dopamine, linked to pleasure, reward, and motivation, also regulates movement and cognitive function. Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin) converts phenylalanine into dopamine, and Vitamin B3 (Niacin) is essential for converting L-tyrosine into dopamine. These B-vitamins contribute to sustaining optimal dopamine levels, fostering a balanced emotional and cognitive state.
Conversion Nutrients:
- Vitamin B2 (Riboflavin): Vitamin B2 converts the amino acid phenylalanine into dopamine, supporting healthy dopamine levels.
- Vitamin B3 (Niacin): Vitamin B3 is necessary to convert the amino acid L-tyrosine into dopamine. It contributes to maintaining optimal dopamine levels.
3. GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid):
GABA (Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid), an inhibitory neurotransmitter, promotes relaxation and reduces anxiety. Vitamin B6 is vital for converting glutamate into GABA, supporting a healthy balance between excitation and inhibition in the brain.
Conversion Nutrients:
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 is essential for converting glutamate into GABA, supporting healthy GABA levels.
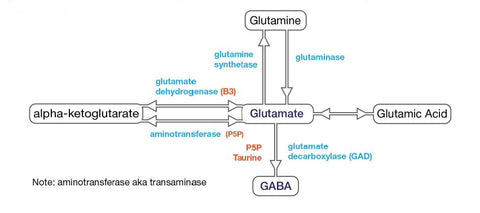
4. Glutamate:
Glutamate, the primary excitatory neurotransmitter, is involved in learning and memory. Vitamin B6 facilitates the conversion of glutamate into GABA, contributing to maintaining a balanced glutamate-GABA ratio.
Conversion Nutrients:
- Vitamin B6: Vitamin B6 is necessary for converting glutamate into GABA. By supporting this conversion, it helps maintain a balanced glutamate-GABA ratio.
5. Acetylcholine:
Acetylcholine, crucial for memory and cognitive function, relies on Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid) for synthesis. This nutrient supports the production and balance of acetylcholine, influencing memory and attention positively.
Conversion Nutrients:
- Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic Acid): Vitamin B5 is required to synthesize acetylcholine. It supports the production and balance of this vital neurotransmitter.
6. Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine):
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine) is involved in stress response, arousal, and attention. Vitamin C aids in converting dopamine into noradrenaline, while iron and copper act as essential cofactors in this conversion, ensuring healthy noradrenaline levels.
Conversion Nutrients:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C plays a role in converting dopamine into noradrenaline. It supports the production and balance of noradrenaline.
- Iron and Copper: Iron and copper are essential cofactors for converting dopamine into noradrenaline. Adequate levels of these minerals support healthy noradrenaline levels.
7. Epinephrine (Adrenaline):
Epinephrine (Adrenaline), released during the fight-or-flight response, increases heart rate and energy levels. Vitamin C supports the conversion of noradrenaline into epinephrine, and Vitamin B12 facilitates the conversion of noradrenaline into epinephrine, ensuring a balanced production of this critical neurotransmitter.
Conversion Nutrients:
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C supports the conversion of noradrenaline into epinephrine, contributing to the production and balance of epinephrine.
- Vitamin B12: Vitamin B12 converts noradrenaline into epinephrine, supporting the synthesis and balance of this neurotransmitter.
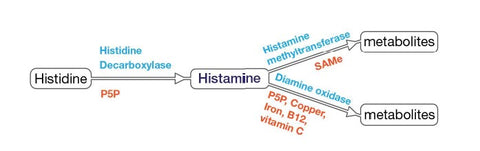
8. Histamine:
Histamine, involved in immune response and wakefulness, plays a role in inflammation. While specific conversion nutrients are not mentioned, a well-balanced diet with a variety of nutrients is essential for overall health, potentially influencing histamine regulation indirectly.
Conversion Nutrients:
- SAM-E: S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM-E) is involved in the methylation process, essential for histamine synthesis. Adequate levels of SAM-E support healthy histamine levels.
- Folate: Folate is a B vitamin that plays a role in histamine metabolism. It supports the conversion and balance of histamine in the body.
Conclusion: Maintaining balanced neurotransmitter levels is crucial for optimal brain health and well-being. Specific nutrients, such as vitamins B2, B3, B5, B6, and B12, iron, copper, vitamin D, vitamin C, SAM-E, and folate, play vital roles in supporting the conversion and balance of neurotransmitters. By ensuring adequate intake of these nutrients through a balanced diet or supplementation, we can help the synthesis, transformation, and balance of neurotransmitters in the brain. However, it's important to note that individual needs may vary, and consulting with a healthcare professional is recommended to determine the appropriate nutrient levels for your specific situation. Prioritizing brain health by nourishing our neurotransmitters can enhance cognitive function, mood, and overall brain vitality.





Leave a comment